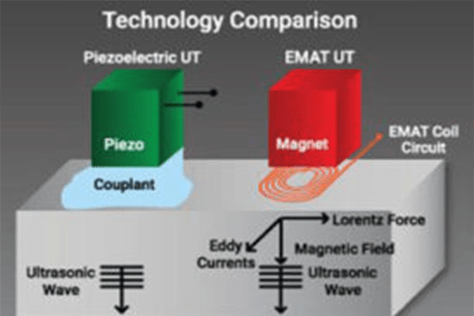
EMAT or Electro Magnetic Acoustic Transducer is an Ultrasonic Testing (UT) technique. An EMAT induces ultrasonic waves into a test object with two interacting magnetic fields. A relatively high frequency (RF) field generated by electrical coils interacts with a low frequency or static field generated by magnets to generate a Lorentz force in a manner similar to an electric motor. Because of the Lorentz force molecules start vibrating and which in turn creates ultrasonic waves. This ultrasonic waves travels through the material and in a reciprocal process, the interaction of elastic waves in the presence of a magnetic field induces currents in the receiving EMAT coil circuit.