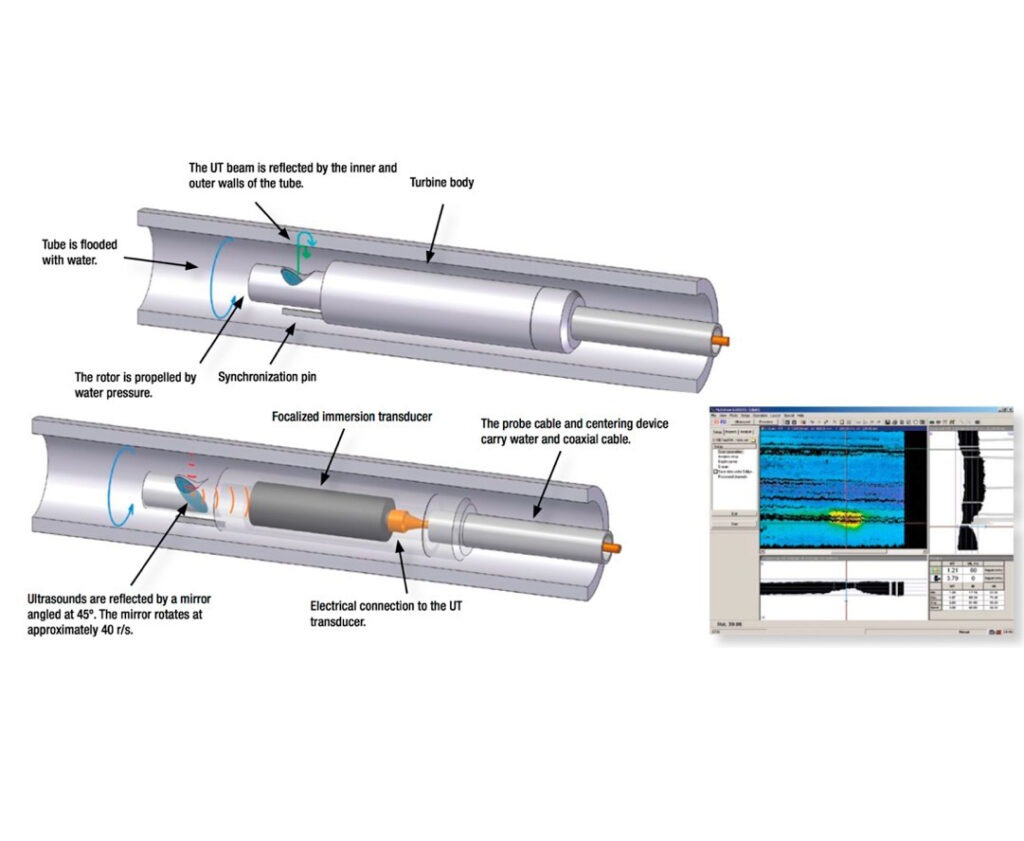
IRIS is an ultrasonic method for the nondestructive inspection of tubes. The IRIS probe is inserted into a tube that is flooded with water, and the probe is pulled out slowly as the data is displayed and recorded. The ultrasonic beam allows detection of metal loss from the inside and outside of the tube wall. IRIS can provide the location of flaw along the length. Defect detection capability for IRIS is better than RFET (in ferrous materials) but it is inferior to ECT (in non-magnetic materials). IRIS is not as capable of detecting smaller defects when compared to ECT. The major disadvantage is that it is very slow technique, but accurate in wall measurement of ferrous tubes in range of 0.15mm. IRIS inspection requires a better cleaning of surface than eddy current testing.