
PAUT is an advanced method of ultrasonic testing. Instead of a single element and beam, phased array uses multiple ultrasonic elements and electronic time delays to create beams by constructive and destructive interference. PAUT offers significant technical advantages for weld testing over conventional ultrasonic as the phased array beams can be steered, scanned, swept and focused electronically from a fixed probe position. Beam steering permits the selected beam angles to be optimized ultrasonically by orienting or focusing them perpendicular to the predicted discontinuities.
PAUT is now used for inspecting fabricated piping and pressure vessel welds. The flaw image obtained with multiple angles and beams give a more accurate flaw characterization than conventional ultrasonic inspection. PAUT can be done in semi-automated or a fully automated mode.
For corrosion mapping application a linear array probe mounted on a wheel is used. Results are immediate, can be viewed as well as emailed for further analysis.
TOFD method of ultrasonic testing is a sensitive and accurate method for the non-destructive testing of welds for defects. The use of TOFD enabled crack sizes to be measured more accurately, and in conjunction with FFS studies, the expensive components could be kept in operation with minimal risk of failure.
Measuring the amplitude of reflected signal is a relatively unreliable method of sizing defects because the amplitude strongly depends on the orientation of the crack. Instead of amplitude, TOFD uses the time of flight of an ultrasonic pulse to determine the position of a reflector.


RVI(boroscopy/Videoscopy) is used to visually inspect plant components for surface defects, general condition, degradation, blockages & foreign materials. It can be used as standalone inspection or as a complement to other NDE techniques, such as eddy current, ultrasonic or x-ray, in order to qualify unclear signals or pinpoint where a more thorough inspection is needed.
We offer a turnkey inspection solutions, whether it is inspecting high energy piping, performing a loose part retrieval or diagnosing an operational problem, we bring the right equipment to visually inspect (or retrieve) it, record it, and report it back to you.

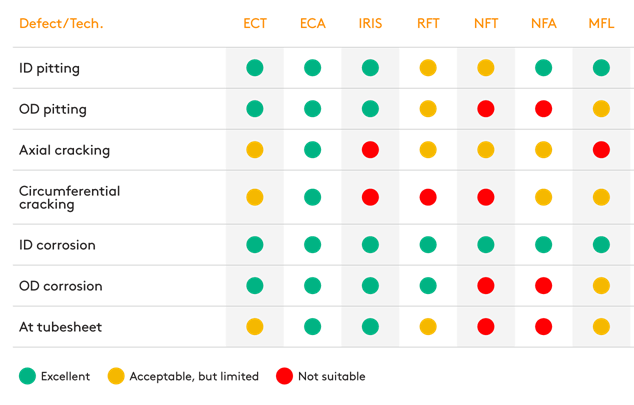
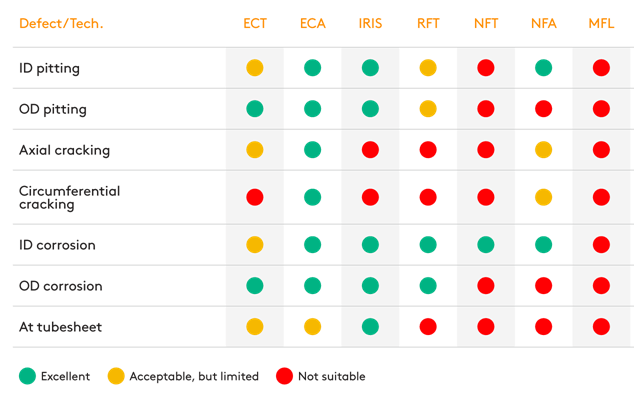

Large number of ferrous steel wire ropes is in use in different industries. Premature discard and replacement with the new rope involves in unreasonable costs, while operating the rope, which already reached discard criteria is dangerous. Visual inspection is obvious, but only visual examination is not sufficient due to specific rope design. Non-destructive magnetic inspection of ropes enables to gather comprehensive data for making reasoned decision. Magnetic flux leakage (MFL) equipment with strong magnetization can inspect ropes reliably, and smart software facilitates data interpretation.
Our rope inspection services comprise inspection of the new ropes either during production run or delivered to the customer, and on-site inspection onshore, offshore, above ground and underground. Inspection is carried in accordance with national / international standards and norms. This enables large cost savings as wire ropes can be used safely for a longer period of time.

Pulse eddy current testing (PECT) is an advance electromagnetic inspection technology which majorly detect remaining wall thickness under insulation in ferrous material. It uses square pulse signal to induced eddy current which can penetrate more deeply in magnetic material than conventional Eddy Currents.
Pulse eddy current testing (PECT) can measure thickness through all insulation materials, coatings, fixed chicken wire, concrete, re-bars, corrosion product, stainless steel sheeting, aluminium sheeting, water marine growth, blistering scabs, through metallic mesh.